Having previously discussed the fundamentals of biotechnology, its impact on the production of medicines and the structure of these protein-based medicines, we now move on to some of the practical aspects of managing therapeutic proteins. In this post we begin our exploration of the storage and handling of biopharmaceuticals. As noted before, because proteins represent the overwhelming majority of products from the pharmaceutical biotechnology sector, … Read More
Biopharmaceutical Protein Structure – Part 2
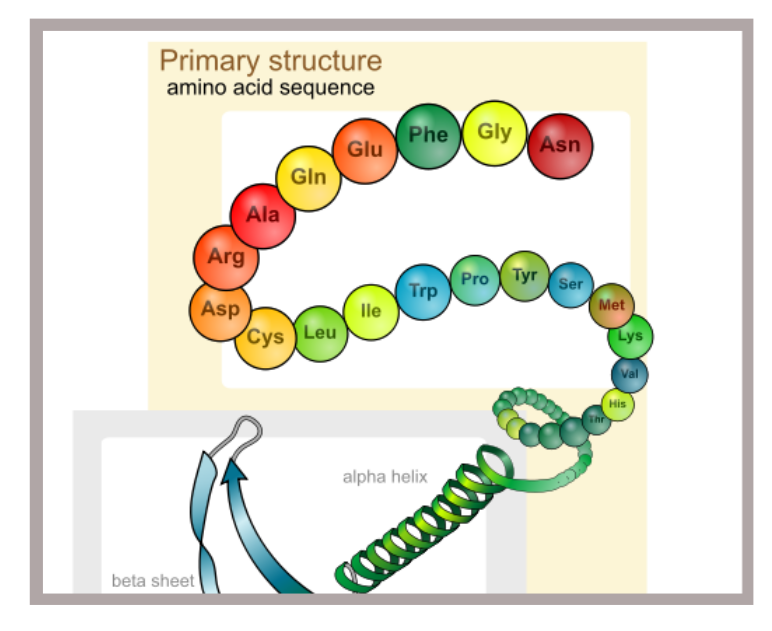
Introduction Our last post entitled, ‘Biopharmaceutical Protein Structure – Part 1‘, looked briefly at the interplay of different chemical bonds common to proteins and their respective contributions to the maintenance of protein structure. We will now apply those principles to the current discussion and explore in greater detail the four levels of protein structure with particular emphasis on the structural complexity of proteins. The Structural Complexity of … Read More
Biopharmaceutical Protein Structure – Part 1
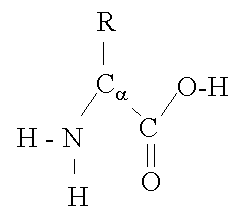
Introduction Given that the overwhelming majority of biopharmaceuticals are proteins, this article will explore some key points on protein structure. This is particularly important because protein function is directly related to protein structure. Specifically we will look at the different types of molecular bonds found in proteins and their relationship to the final three-dimensional configuration of said proteins. If we are to appreciate … Read More
Classification of Pharmaceuticals: Biologics vs. Conventional Medicines
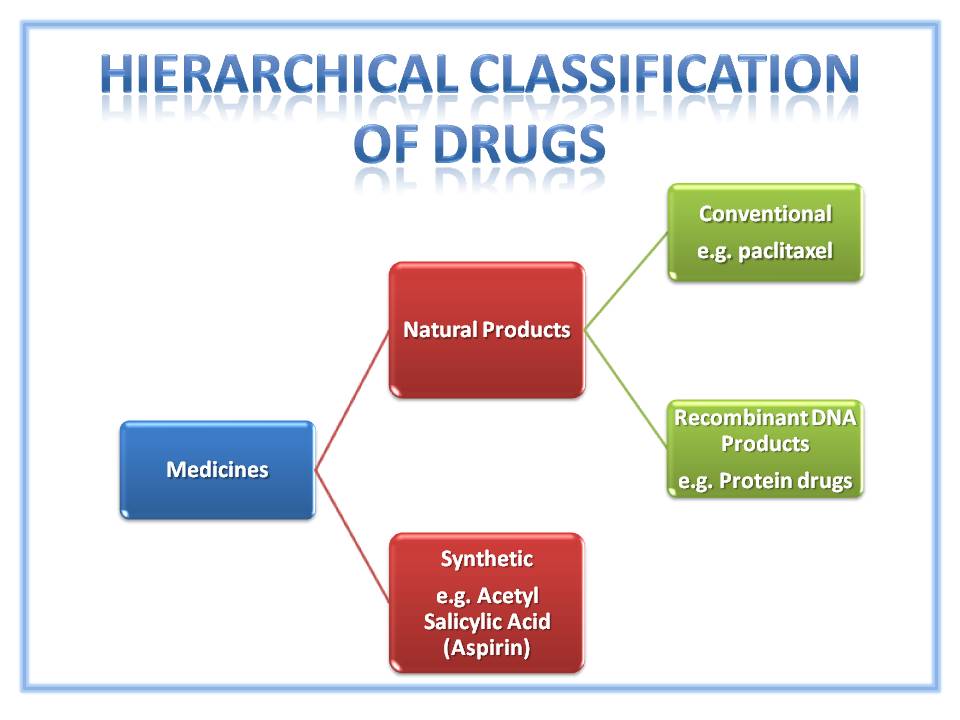
Introduction Medicines can be separated into two broad groups. The first is ‘Synthetic Medicines‘. As the name suggests they are created through supervised chemical synthesis. The associated chemical reactions are relatively simple and often sequential. The final active substances produced are small molecules with relatively simple chemical structures, an example being aspirin (Figure 2). Natural Products By contrast natural products are derived from comparatively complex starting materials sourced from the ‘Natural Environment‘. More specifically, they are derived from … Read More
What is a Biopharmaceutical? (Part II): Biopharmaceutical Characteristics
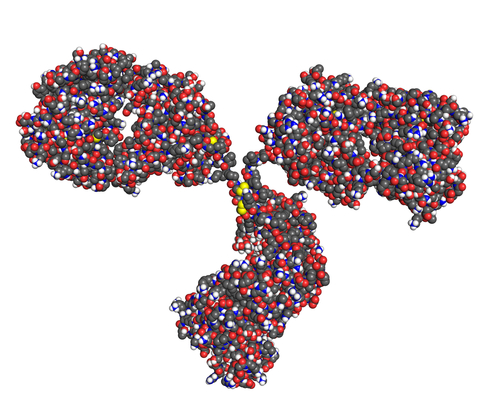
The following list while not comprehensive, provides some key characteristics of biopharmaceuticals / biologics: 1. They are produced within ‘Living Cells’. 2. They are proteins in most cases although more recent developments have seen nucleic acids entering the fray as therapeutic agents. 3. They have very large molecular weights and by extension tend to be very large molecules. (This is … Read More